Researchers from the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center have made significant strides in understanding and potentially overcoming resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).
Their study, titled "Pharmacological modulation of RB1 activity mitigates resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer", was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).

Screenshot from the website of PNAS.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is the primary method of downstaging tumor and improving treatment outcomes in patients with LARC. However, a considerable number of patients develop resistance to this treatment, leading to unfavorable prognoses. Recognizing the urgent need to delve into the molecular mechanisms behind resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in rectal cancer, the research team embarked on a journey to uncover potential therapeutic targets and develop novel treatment strategies.
By characterizing the molecular features of neoadjuvant chemotherapy-resistant rectal cancer and employing high-throughput drug screening, the researchers identified that CDK4/6 inhibitors could effectively enhance the efficacy of oxaliplatin. Furthermore, leveraging multi-omics sequencing techniques such as whole transcriptome sequencing and epigenetic profiling, they elucidated the underlying molecular mechanisms.
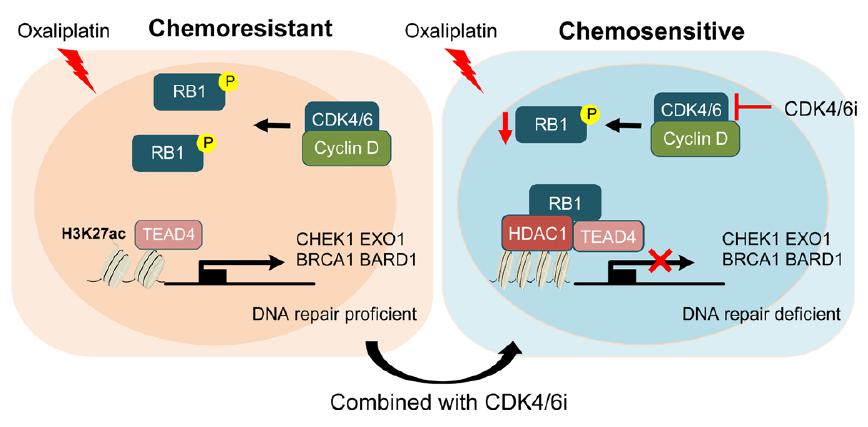
CDK4/6 inhibitors reverse oxaliplatin resistance by influencing epigenetic modifications that regulate the expression of homologous recombination repair-associated genes.
This research opens up new avenues for the treatment of neoadjuvant chemotherapy-resistant rectal cancer. The identification of CDK4/6 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents and the elucidation of associated molecular mechanisms offer promising prospects for improving treatment outcomes for the patients with this condition.
It represents a significant step forward in the quest to improve the management of LARC and underscores the importance of molecular research in combating treatment resistance.
Author | Hannah
Editor | Steven, Monica, James
Source | The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University
















